티스토리 뷰
Compose UI는 Compose Runtime의 기능을 활용하여 실제 UI 노드 트리(레이아웃 트리)를 생성하고 업데이트합니다.
Compose UI의 특징
- Compose UI는 클라이언트 라이브러리입니다.
- Kotlin 멀티플랫폼 기반이며, Android/데스크톱 통합 계층을 포함합니다.
- Compose 런타임은 UI나 플랫폼(Android 등)에 대해 알지 못하며 독립적입니다.
- 런타임은 노드 변경 작업을 클라이언트(UI)에 위임하며, Compose UI는 이를 위해 LayoutNode 노드타입을 사용합니다.
레이아웃 트리 구축 및 변경 사항 위임
- Composition과 Recomposition 과정은 Composable 함수를 실행하여 레이아웃 트리를 구축하고 업데이트합니다.
- Composable 함수는 실행 시 LayoutNode를 emit하여 UI 변경 사항을 예약하는데, 이때 ReusableComposeNode를 사용합니다.
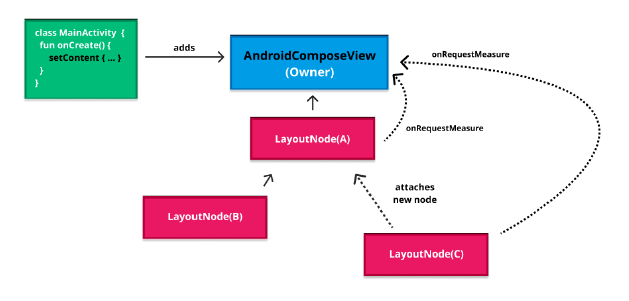
- 노드를 삽입, 제거, 이동하는 모든 작업은 LayoutNode 자체에 위임됩니다. 이 과정에서 LayoutNode는 부모 Owner(AndroidComposeView)에 연결되고, Owner를 통해 안드로이드 View API를 사용하여 무효화(invalidation)가 트리거됩니다. 이 무효화 요청은 다음 그리기 단계에서 노드의 재측정, 배치, 그리기를 유발하여 최종 UI 변경 사항을 화면에 반영합니다.
- 런타임은 변경 사항을 Applier(Android: UiApplier)에 전달하고, Applier는 이를 실제 UI 트리에 반영합니다. 이 과정을 구체화(materialization)라고 합니다.
internal class LayoutNode(
private val isVirtual: Boolean = false,
override var semanticsId: Int = generateSemanticsId(),
) :
ComposeNodeLifecycleCallback,
Remeasurement,
OwnerScope,
LayoutInfo,
SemanticsInfo,
ComposeUiNode,
InteroperableComposeUiNode,
Owner.OnLayoutCompletedListener {
/**
* 이 LayoutNode의 자식들입니다. [insertAt], [move], [removeAt]에 의해 관리됩니다.
*/
internal val children: List<LayoutNode>
get() = _children.asMutableList()
/**
* LayoutNode 계층에서 이 노드의 부모입니다.
* 이 LayoutNode가 계층에 속해있지 않거나 루트인 경우에는 `null`입니다.
*/
private var _foldedParent: LayoutNode? = null
/**
* LayoutNode 계층에서의 부모 노드입니다. 단, 가상 노드는 건너뜁니다.
*/
internal val parent: LayoutNode?
get() {
var parent = _foldedParent
while (parent?.isVirtual == true) {
parent = parent._foldedParent
}
return parent
}
/**
* View 시스템의 [Owner]입니다.
* 이 값은 [attach]가 호출되기 전까지는 `null`입니다.
*/
internal var owner: Owner? = null
private set
/**
* LayoutNode 내부 레이아웃 동작을 위임받는 구조입니다.
*/
internal val layoutDelegate: LayoutNodeLayoutDelegate = LayoutNodeLayoutDelegate(this)
}internal class LayoutNodeLayoutDelegate(internal val layoutNode: LayoutNode) {
val outerCoordinator: NodeCoordinator
get() = layoutNode.nodes.outerCoordinator
val lastConstraints: Constraints?
get() = measurePassDelegate.lastConstraints
val lastLookaheadConstraints: Constraints?
get() = lookaheadPassDelegate?.lastConstraints
internal val height: Int
get() = measurePassDelegate.height
internal val width: Int
get() = measurePassDelegate.width
internal var layoutState = LayoutState.Idle
fun updateParentData() {
if (measurePassDelegate.updateParentData()) {
layoutNode.parent?.requestRemeasure()
}
if (lookaheadPassDelegate?.updateParentData() == true) {
if (layoutNode.isOutMostLookaheadRoot) {
layoutNode.parent?.requestRemeasure()
} else {
layoutNode.parent?.requestLookaheadRemeasure()
}
}
}
fun invalidateParentData() {
measurePassDelegate.invalidateParentData()
lookaheadPassDelegate?.invalidateParentData()
}
fun resetAlignmentLines() {
measurePassDelegate.alignmentLines.reset()
lookaheadPassDelegate?.alignmentLines?.reset()
}
fun markChildrenDirty() {
measurePassDelegate.childDelegatesDirty = true
lookaheadPassDelegate?.let { it.childDelegatesDirty = true }
}
//...
}
ReusableComposeNode
ReusableComposeNode는 같은 key를 가진 노드를 삭제하지 않고 재사용하며, 내용만 갱신(recompose)하여 성능을 최적화하는 Compose Runtime 기능입니다. 내부적으로는 SlotTable을 탐색해 기존 노드를 찾아 활용합니다.
ReusableComposeNode는 내부 상태가 없는 단순한 노드만 재사용할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, LayoutNode는 가능하지만, AndroidView는 복잡한 내부 상태 때문에 재사용되지 않고 일반 ComposeNode를 사용합니다.
ReusableComposeNode는 다음과 같은 방식으로 사용됩니다.
- factory 함수로 노드를 생성합니다.
- 생성된 노드는 update 블록에서 modifier, measurePolicy 등의 속성을 설정합니다.
- 내부적으로는 하나의 replaceable group(교체 가능한 그룹)을 만들고, 여기에 고유 키(key)를 부여합니다. 이 키를 통해 나중에 해당 노드를 식별하고 재사용할 수 있게 됩니다.
- content 블록 안에서 자식 노드들이 정의되며, 이들은 모두 해당 replaceable group의 자식으로 포함됩니다.
- update 블록 안의 set 호출은, 해당 속성이 실제로 변경되었을 때만 적용됩니다. 불필요한 업데이트를 방지하여 성능을 높입니다.
@Composable
@UiComposable
inline fun Layout(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
measurePolicy: MeasurePolicy
) {
val compositeKeyHash = currentCompositeKeyHash
val materialized = currentComposer.materialize(modifier)
val localMap = currentComposer.currentCompositionLocalMap
ReusableComposeNode<ComposeUiNode, Applier<Any>>(
factory = ComposeUiNode.Constructor,
update = {
set(measurePolicy, SetMeasurePolicy)
set(localMap, SetResolvedCompositionLocals)
set(materialized, SetModifier)
set(compositeKeyHash, SetCompositeKeyHash)
},
)
}
@Composable inline fun <T : Any, reified E : Applier<*>> ReusableComposeNode(
noinline factory: () -> T,
update: @DisallowComposableCalls Updater<T>.() -> Unit
) {
if (currentComposer.applier !is E) invalidApplier()
currentComposer.startReusableNode()
if (currentComposer.inserting) {
currentComposer.createNode(factory)
} else {
currentComposer.useNode()
}
Updater<T>(currentComposer).update()
currentComposer.endNode()
}
Composition 및 Subcomposition의 관리
Compose UI는 런타임의 Applier, Composition, Recomposition 메커니즘을 구현하여 플랫폼에 구애받지 않는 방식으로 Composable의 선언적 UI 정의를 최종 화면의 시각적 요소로 변환합니다.
- 루트 Composition은 setContent 호출로 생성되며, 독립적인 Composable 트리를 관리합니다. 앱은 여러 루트 Composition을 가질 수 있습니다.
- Subcomposition은 Composable 내부에서 생성되는 하위 Composition이며, 상위 Composition과 CompositionContext로 연결됩니다.
- Compose UI는 Applier, Composition, Recomposition을 활용해 선언적 UI를 실제 화면으로 변환합니다.
Composition 생성의 진입점과 메커니즘
setContent 호출은 Compose UI 라이브러리에서 Compose 런타임으로의 가장 빈번한 진입점을 나타냅니다.
- ViewGroup.setContent 호출은 새로운 Composition 인스턴스를 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. Composition을 생성할 때는 UiApplier 인스턴스와 부모 CompositionContext가 전달됩니다.
- setContent는 여러 개의 독립적인 Composable 트리를 호스팅하는 역할을 하며, 호출될 때마다 루트 Composition을 생성하고 가능한 경우 재사용합니다. Activity, Fragment, ComposeView 등 다양한 위치에서 호출될 수 있으며, 각 Composition은 서로 독립적입니다.

// 1
public fun ComponentActivity.setContent(
parent: CompositionContext? = null,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
val existingComposeView = window.decorView
.findViewById<ViewGroup>(android.R.id.content)
.getChildAt(0) as? ComposeView
if (existingComposeView != null) with(existingComposeView) {
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
} else ComposeView(this).apply {
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
setOwners()
setContentView(this, DefaultActivityContentLayoutParams)
}
}
// 2
class ComposeView @JvmOverloads constructor(
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet? = null,
defStyleAttr: Int = 0
) : AbstractComposeView(context, attrs, defStyleAttr) {
private val content = mutableStateOf<(@Composable () -> Unit)?>(null)
@Suppress("RedundantVisibilityModifier")
protected override var shouldCreateCompositionOnAttachedToWindow: Boolean = false
private set
@Composable
override fun Content() {
content.value?.invoke()
}
override fun getAccessibilityClassName(): CharSequence {
return javaClass.name
}
fun setContent(content: @Composable () -> Unit) {
shouldCreateCompositionOnAttachedToWindow = true
this.content.value = content
if (isAttachedToWindow) {
createComposition()
}
}
}
// 3 (AbstractComposeView)
fun createComposition() {
check(parentContext != null || isAttachedToWindow) {
"createComposition requires either a parent reference or the View to be attached" +
"to a window. Attach the View or call setParentCompositionReference."
}
ensureCompositionCreated()
}
// 4 (AbstractComposeView)
private fun resolveParentCompositionContext() = parentContext
?: findViewTreeCompositionContext()?.cacheIfAlive()
?: cachedViewTreeCompositionContext?.get()?.takeIf { it.isAlive }
?: windowRecomposer.cacheIfAlive()
@Suppress("DEPRECATION") // Still using ViewGroup.setContent for now
private fun ensureCompositionCreated() {
if (composition == null) {
try {
creatingComposition = true
composition = setContent(resolveParentCompositionContext()) {
Content()
}
} finally {
creatingComposition = false
}
}
}
Subcomposition
Subcomposition은 루트가 아닌 Composable 트리의 내부에서 생성되는 독립적인 Composition 인스턴스입니다. setContent로 생성되는 루트 Composition과 달리, Subcomposition은 더 깊은 UI 계층에서 생성됩니다.
- 상위 Composition과의 연결: Subcomposition은 독립적으로 구성되지만, 부모 CompositionContext를 통해 상위 Composition과 연결되어, 무효화, CompositionLocal 전파, 재구성 타이밍 등이 루트 Composition과 함께 연동됩니다.
- 레이아웃 의존 구성 지연: 부모의 크기나 제약조건 같은 레이아웃 정보를 알아야 하는 콘텐츠는 SubcomposeLayout이나 BoxWithConstraints처럼 Subcomposition을 사용해 레이아웃 계산 단계에서 나중에 구성됩니다.
- 노드 타입 변경: 메인 트리와 다른 노드 타입이 필요한 경우, 예를 들어 VectorPainter처럼 VNode를 사용하는 경우에는 별도의 Subcomposition이 생성되며, 이에 맞는 Applier(VNode: VectorApplier)가 사용됩니다.
@Composable
fun rememberVectorPainter(image: ImageVector): VectorPainter {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val key = packFloats(image.genId.toFloat(), density.density)
return remember(key) {
createVectorPainterFromImageVector(
density,
image,
GroupComponent().apply {
createGroupComponent(image.root)
}
)
}
}
- 생성과 생명주기 관리: rememberCompositionContext()를 통해 현재 위치의 CompositionContext를 기억하거나 가져와 Subcomposition을 생성하고, 수명이 끝나면 composition.dispose()로 명시적으로 폐기하며, 이 과정은 DisposableEffect 등을 통해 자동으로 관리할 수 있습니다.
- ReusableComposition: 여러 콘텐츠를 교체하면서 재사용할 수 있는 Subcomposition
- PausableComposition: 프레임 사이에 나눠서 실행 가능한 일시정지 가능한 Subcomposition
// Composable.kt
@Composable fun rememberCompositionContext(): CompositionContext {
return currentComposer.buildContext()
}// SubComposition.kt
internal expect fun createApplier(container: LayoutNode): AbstractApplier<LayoutNode>
/*@MainThread*/
internal fun createSubcomposition(
container: LayoutNode,
parent: CompositionContext,
): ReusableComposition = ReusableComposition(createApplier(container), parent)
internal fun createPausableSubcomposition(
container: LayoutNode,
parent: CompositionContext,
): PausableComposition = PausableComposition(createApplier(container), parent)/**
* 재사용 가능한 Composition으로, 콘텐츠를 바꿔가며 쓸 수 있습니다.
* 부모-자식 Composition의 생명주기 동기화나 ReusableComposeNode 재사용에 사용됩니다.
*/
public sealed interface ReusableComposition : Composition {
/**
* 현재 Composition을 재사용 모드로 전환한 후, 새로운 Composable 콘텐츠를 설정합니다.
* 기존 remember 상태는 모두 제거되며, 그룹 구조가 같다면 노드는 재사용됩니다.
* 이미 dispose된 Composition에서 호출하면 예외가 발생합니다.
*/
public fun setContentWithReuse(content: @Composable () -> Unit)
/**
* remember된 상태와 관찰 스코프는 제거하되, 노드는 그대로 유지합니다.
* 이후 setContent로 다시 사용할 수 있습니다.
*/
public fun deactivate()
}/**
* [PausableComposition]은 일시정지/재개 가능한 하위 Composition입니다.
* 예: LazyList 항목을 미리 준비할 때, 프레임 사이에 Composition을 분산시켜 성능을 최적화합니다.
* [apply()] 전까지는 결과를 레이아웃 트리에 사용하면 안 됩니다.
* 일반 Composition처럼 쓰면 예외가 발생할 수 있습니다.
*/
public sealed interface PausableComposition : ReusableComposition {
/**
* 일시정지된 상태로 콘텐츠를 설정합니다.
* [resume()]을 반복 호출해 [isComplete]가 true가 되면 [apply()]로 완성시켜야 사용 가능합니다.
*/
public fun setPausableContent(content: @Composable () -> Unit): PausedComposition
/**
* 재사용 가능한 Composition으로 콘텐츠를 일시정지 상태로 설정합니다.
* 역시 [resume()] → [apply()]까지 완료되어야 사용 가능합니다.
*/
public fun setPausableContentWithReuse(content: @Composable () -> Unit): PausedComposition
}
구체화 (Materialization)
구체화는 Compose 런타임이 계산한 UI 변경 사항을 LayoutNode 기반의 실제 UI 트리로 변환하고, 이를 Android View 시스템 같은 플랫폼에 연결해 사용자에게 시각적으로 표시하는 과정입니다. 이 작업은 Applier 추상화가 핵심 역할을 수행합니다.
- 변경 사항의 기록 및 Applier로의 위임: Composition 또는 Recomposition 시, Composable 함수 실행 결과로 UI 변경 사항(삽입, 삭제, 교체 등)이 예약된 변경 목록(scheduled changes) 형태로 생성됩니다. 이 목록은 Applier에게 전달되고, Applier는 이를 감지하여 실제 LayoutNode 트리에 반영합니다. Applier는 런타임과 플랫폼 사이의 추상화 계층으로, UI 변경을 실행하는 역할을 클라이언트(UI 라이브러리)에 위임합니다.
- Compose UI의 Applier 구현체 및 노드 연결: Compose UI는 UiApplier를 통해 LayoutNode 기반의 UI 트리를 관리하며, 안드로이드 View 시스템과 연결합니다. LayoutNode는 Kotlin으로만 작성된 UI 노드이며, Android 플랫폼에 대한 의존성이 없습니다. Applier는 노드 조작(삽입, 이동, 삭제 등)을 LayoutNode에게 위임하여, Compose 런타임이 직접 플랫폼을 알지 않고도 UI를 구체화할 수 있게 합니다.

- 노드 삽입 전략 및 성능 최적화: UiApplier는 노드를 삽입할 때 상향식(bottom-up) 전략을 사용합니다. 이 방식은 insertTopDown()을 무시하고 항상 insertBottomUp()만 사용하는데, 이는 자식 노드 삽입 시 부모에게만 직접 알림을 보내 중첩 구조에서 중복 호출을 줄이고 성능을 높이는 데 유리합니다.
- 최종 UI 반영 (Attaching and Drawing): 구체화의 마지막 단계에서는 LayoutNode가 Owner(안드로이드에서는 AndroidComposeView)에 연결되어 플랫폼 뷰와 통합됩니다. 이 Owner는 View 시스템과의 연결 지점 역할을 하며, LayoutNode는 이를 통해 Android View API를 호출하여 무효화(invalidation)를 트리거합니다. 이 무효화는 다음 그리기 프레임에서 dispatchDraw()를 통해 재측정, 레이아웃, 드로잉 순으로 실행되어 최종 UI가 화면에 반영됩니다.
'Android > Compose' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Compose UI(2) - Measuring, Modifier (0) | 2025.11.02 |
|---|---|
| Compose Runtime(2) - Applier, Composition, Recomposer (0) | 2025.03.30 |
| Compose Runtime(1) - Composer, SlotTable, ChangeList (0) | 2025.03.30 |
